Using the ‘Set Temporary IP Address Tool’ in Emerson’s Proficy Machine Edition.
Emerson Proficy Machine Edition has many useful tools to assist in troubleshooting and fast deployment. However, there is one tool in particular to give you the ability to set the IP address and download a configuration temporarily to the device.
Step One
Under the Tools and Utilities tab select ‘Set Temporary IP Address’ and enter the MAC ID on the Emerson device you wish to assign to. Connect and then assign your PC to the same IP range.
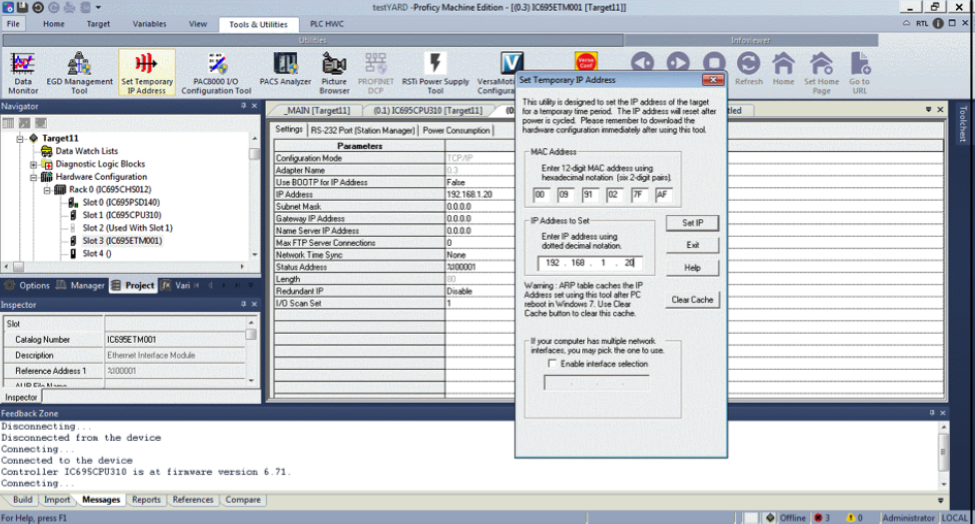
Step Two
Hit the Set IP button and a pop-up window will appear, press OK.
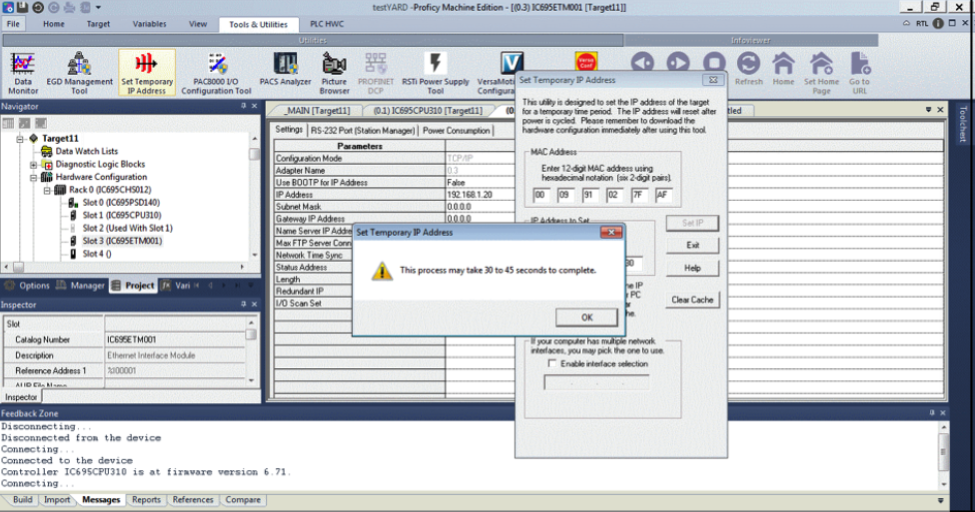
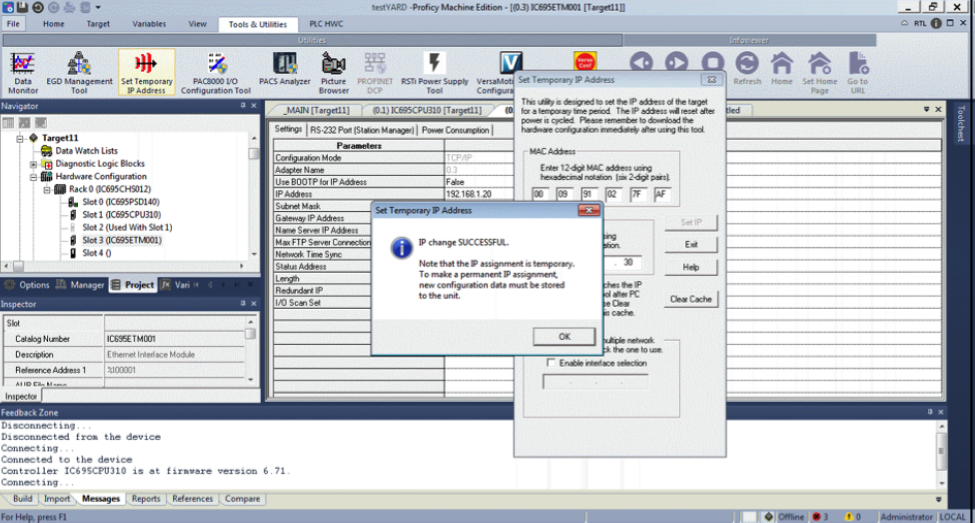
When successful, a pop-up window will appear.
Ensure you download a configuration, as the setting is only temporary.
|